Common myeloid precursor (CMP) cells are stem cells that can either differentiate into an erythroid (red blood cell) cell or a myeloid (bone marrow) cell. Such a binary differentiation may be regulated by a genetic circuit akin to the toggle circuits we have already encountered. However, the progenitor state of the CMP cells is also stable, which suggests tristability of the underlying circuit. In particular, the transcription factors GATA1 (which we will call X for convenience) and PU.1 (which we will call Y) are mutually repressive, which gives them the toggle-like behavior. They also are autoactivating. These interactions are summarized in the circuit below.
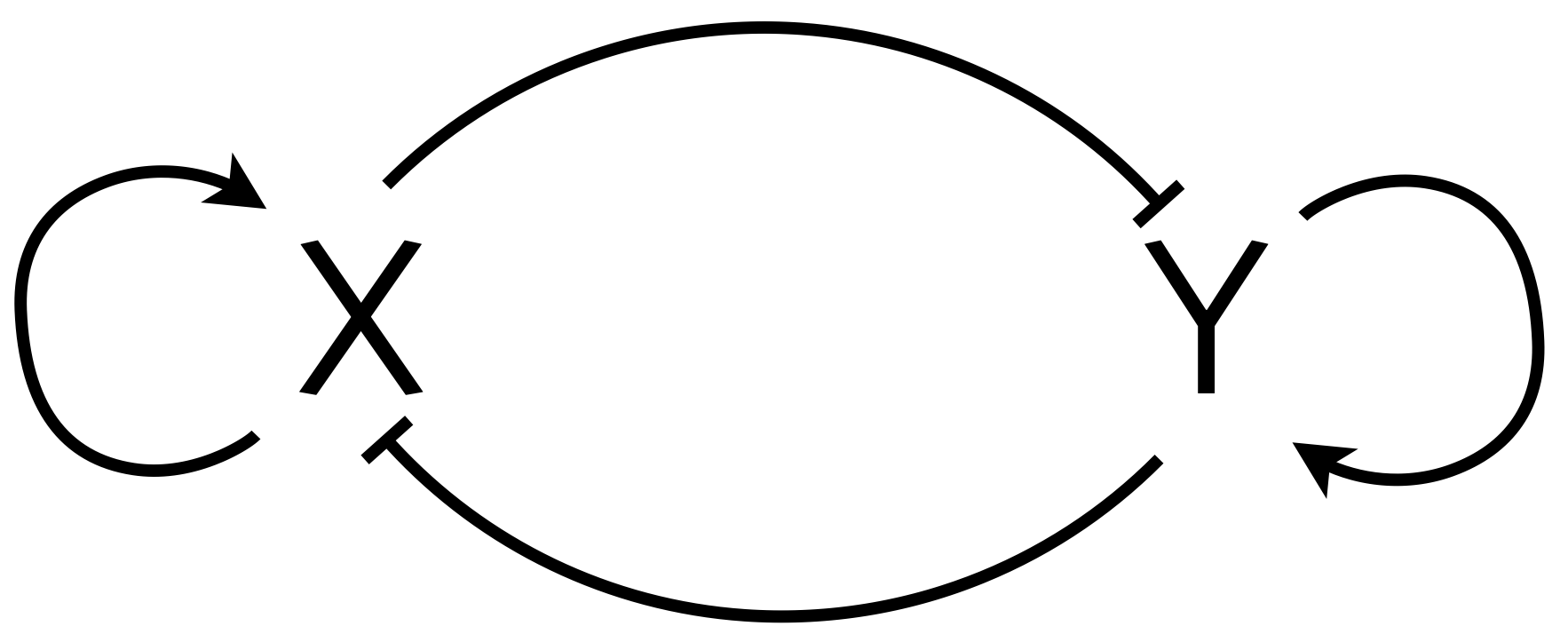
Huang and coworkers (Dev. Biol., 2007) claimed that this circuit can give tristability. Your task is to assess that claim. Model the circuit where the repression of X by Y and X's autoactivation exhibits OR logic as does repression of Y by X and Y's autoactivation. Can you come up with parameter values that show tristability? Hint: Think about how many fixed points are necessary to get tristability.
To verify the tristability, you can do a graphical analysis using nullclines. Alternatively, if you find parameter values that give enough fixed points for tristability, you can numerically perform a linear stability analysis for each fixed point.
Here is another useful hint: It may be a bit tricky to plot the nullclines because they may be discontinuous and not defined on some intervals. Make sure you plot plenty of values of $x$ and $y$ so that you can catch all of the crossings of nullclines.